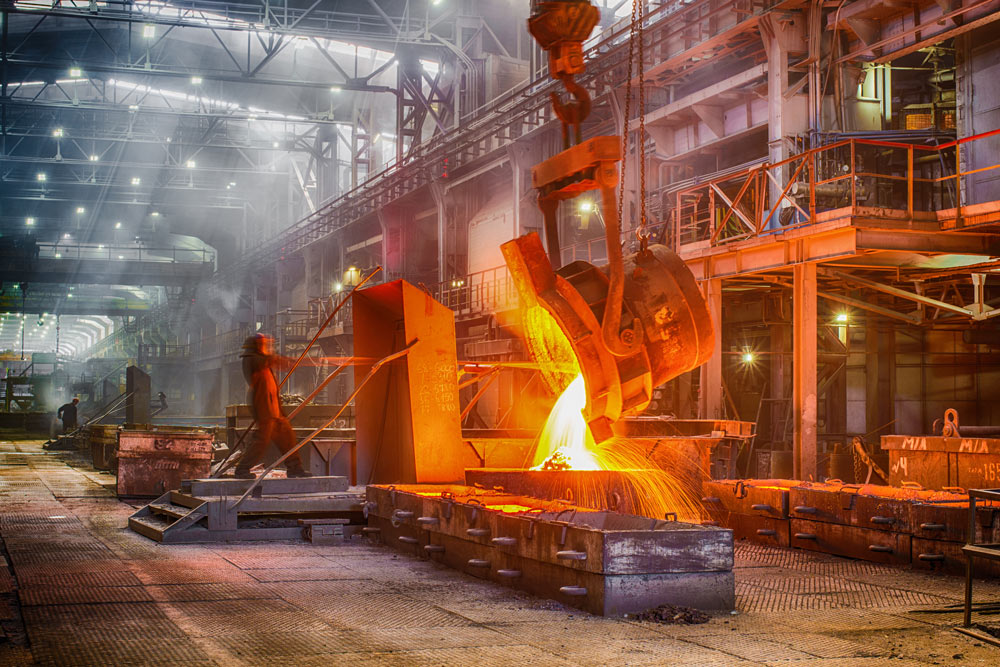
Safety is paramount in the steel industry, where workers are exposed to various hazards during the production and processing of steel. Conveyor belts are integral to steel manufacturing processes, facilitating the movement of raw materials, finished products, and by-products throughout the facility. However, conveyor belts pose safety risks if not properly guarded and monitored. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the importance of conveyor belt guarding and monitoring solutions in enhancing safety within the steel industry.
The Importance of Safety in the Steel Industry: The steel industry is known for its high-risk environment, with potential hazards including moving machinery, heavy equipment, high temperatures, and exposure to hazardous materials. Ensuring the safety of workers is not only a legal requirement but also a moral obligation for steel manufacturers. Accidents involving conveyor belts can result in serious injuries, fatalities, and costly downtime, making safety measures a top priority in steel production facilities.
Conveyor Belt Guarding: Preventing Accidents at the Source Conveyor belt guarding is a crucial aspect of safety management in the steel industry, as it helps prevent accidents and injuries by eliminating or minimizing contact with moving parts of conveyor systems. Guarding solutions are designed to cover exposed conveyor belt components such as pulleys, rollers, and nip points, reducing the risk of entanglement, crushing, and impact injuries. Some common types of conveyor belt guarding include:
- Fixed Guards: Fixed guards are permanent barriers installed along conveyor belts to prevent access to hazardous areas. These guards are typically constructed from durable materials such as steel or polycarbonate and are designed to withstand impact and environmental conditions.
- Interlocked Guards: Interlocked guards are equipped with safety switches or sensors that automatically shut down conveyor belts when the guard is opened or tampered with. This ensures that workers cannot access hazardous areas while the conveyor is in operation, reducing the risk of accidents and injuries.
- Adjustable Guards: Adjustable guards can be customized to fit different conveyor belt configurations and are designed to allow easy access for maintenance and cleaning while providing adequate protection against moving parts. These guards can be adjusted to accommodate changes in conveyor belt layout or equipment configuration.
- Barrier Guards: Barrier guards are physical barriers installed along the sides of conveyor belts to prevent workers from accidentally stepping onto the conveyor or falling off the edge. These guards help maintain a safe distance between workers and moving conveyor belts, reducing the risk of falls and collisions.
Conveyor Belt Monitoring: Early Detection of Issues In addition to guarding solutions, conveyor belt monitoring systems play a crucial role in safety management by providing real-time data on the condition and performance of conveyor belts. Monitoring systems use sensors, cameras, and other technologies to detect abnormalities, such as belt misalignment, slippage, and wear, allowing maintenance personnel to take proactive measures before issues escalate. Some common types of conveyor belt monitoring solutions include:
- Belt Alignment Sensors: Belt alignment sensors detect misalignment between conveyor belts and pulleys, which can cause excessive wear and tear and increase the risk of belt damage or failure. By continuously monitoring belt alignment, these sensors ensure smooth operation and prevent costly downtime.
- Speed Sensors: Speed sensors measure the speed of conveyor belts and detect fluctuations that may indicate belt slippage or overloading. By monitoring belt speed, these sensors help prevent accidents caused by sudden stops or jams and ensure optimal conveyor performance.
- Temperature Sensors: Temperature sensors monitor the temperature of conveyor belts and detect overheating, which can indicate friction or mechanical issues. By alerting maintenance personnel to potential problems, these sensors help prevent belt fires and other safety hazards.
- Wear Monitoring Systems: Wear monitoring systems use sensors or cameras to assess the condition of conveyor belts and detect signs of wear, damage, or corrosion. By identifying areas of concern early on, these systems allow maintenance personnel to schedule timely repairs or replacements, minimizing the risk of belt failure and ensuring worker safety.
Case Study: Steel Manufacturing Plant To illustrate the effectiveness of conveyor belt guarding and monitoring solutions in enhancing safety within the steel industry, let’s consider a case study of a steel manufacturing plant. In such facilities, conveyor belts are used to transport raw materials, molten steel, and finished products throughout the production process. By implementing comprehensive guarding and monitoring solutions, the plant can prevent accidents, reduce downtime, and protect workers from harm, ultimately improving safety performance and operational efficiency.
Conclusion: In conclusion, conveyor belt guarding and monitoring solutions play a critical role in enhancing safety within the steel industry. By preventing accidents at the source through effective guarding and providing early detection of issues through advanced monitoring technologies, these solutions help protect workers, prevent costly downtime, and ensure compliance with safety regulations. As the steel industry continues to evolve and innovate, investing in comprehensive conveyor belt safety measures remains essential for safeguarding workers and achieving sustainable growth. By prioritizing safety, steel manufacturers can create a safer, more productive work environment for their employees and contribute to the overall success and sustainability of the industry.